Esophagus Disease Treatments by Dr. Koushik Podduturi
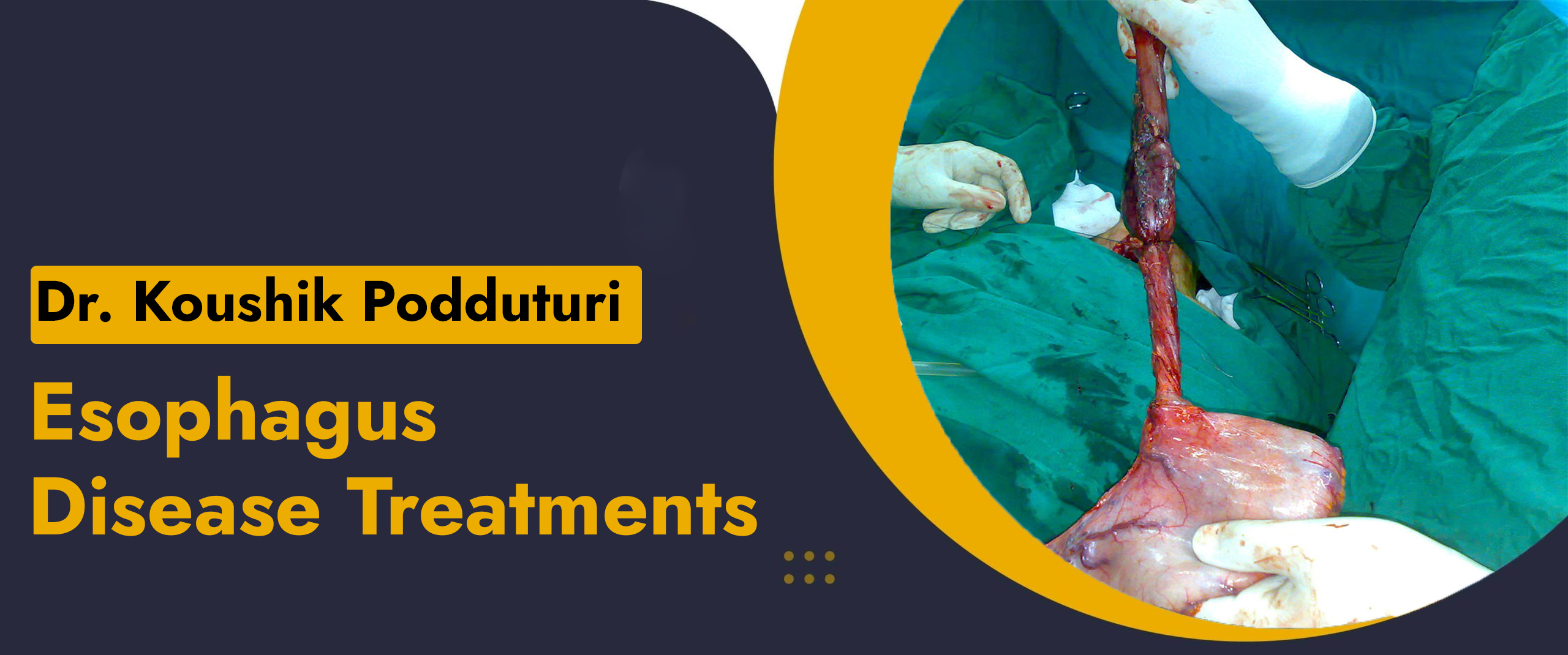
Esophageal diseases encompass a range of conditions affecting the esophagus, the muscular tube that connects the throat to the stomach. These conditions can include disorders such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), Barrett's esophagus, esophageal cancer, esophageal strictures, esophageal motility disorders, and esophageal diverticula. Surgeons who specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of esophageal diseases are typically known as Surgical gastroenterologist or upper gi surgeons
Esophageal surgeons have expertise in a variety of surgical procedures related to esophageal diseases. These procedures may include:
- Fundoplication: A surgical procedure to treat severe GERD by reinforcing the lower esophageal sphincter, which helps prevent acid reflux.
- Esophagectomy: Surgical removal of all or part of the esophagus, often performed to treat esophageal cancer.
- Esophageal Resection and Reconstruction: Removal of a portion of the esophagus followed by reconnecting the remaining healthy sections.
- Stricture Dilation: A procedure to widen narrowed sections of the esophagus using a balloon or other devices.
- Stent Placement: Placement of a stent to help keep the esophagus open and alleviate symptoms of strictures or tumors.
- Laparoscopic and Minimally Invasive Techniques: Some esophageal surgeries can be performed using minimally invasive approaches, such as laparoscopic or robotic-assisted techniques, which may offer faster recovery and reduced scarring.

Esophageal diseases can present with a variety of symptoms, which can vary depending on the specific condition. Here are some common symptoms associated with esophageal diseases:
- Heartburn: This is a burning sensation or discomfort in the chest that often occurs after eating and may be accompanied by regurgitation of stomach acid. Heartburn is a hallmark symptom of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
- Dysphagia: Difficulty swallowing or the sensation of food getting stuck in the throat or chest. Dysphagia can be a symptom of esophageal strictures, esophageal tumors, or motility disorders such as achalasia.
- Odynophagia: Painful swallowing, which can be caused by various esophageal conditions, including esophagitis (inflammation of the esophagus), infections, or certain medications.
- Chest pain: Esophageal diseases, such as GERD or esophageal spasms, can cause chest pain that may be mistaken for a heart-related issue. It is important to differentiate between esophageal and cardiac causes of chest pain.
- Regurgitation: The backflow of undigested food or stomach contents into the mouth, often accompanied by a sour or bitter taste. It can occur in GERD or other esophageal motility disorders.
- Chronic cough: A persistent cough that may be related to the reflux of stomach acid into the esophagus and throat, known as laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR).
- Hoarseness or voice changes: Irritation of the throat and vocal cords caused by acid reflux can lead to hoarseness, voice changes, or a persistent sore throat.
- Unintentional weight loss: Significant and unexplained weight loss can occur in advanced stages of esophageal cancer or other serious esophageal conditions.
- Chest discomfort or pressure: Esophageal conditions such as esophageal spasms or esophageal motility disorders can cause non-cardiac chest pain or a feeling of pressure in the chest.
- Vomiting blood or black, tarry stools: These are signs of gastrointestinal bleeding, which can occur with esophageal varices, ulcers, or advanced esophageal cancer.
- It's important to note that these symptoms are not exclusive to esophageal diseases and can be caused by various other conditions. If you are experiencing persistent or concerning symptoms, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
The management of esophageal diseases depends on the specific condition and its underlying causes. Here is an overview of some common esophageal diseases and their management strategies:
-
1. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD):
- • Lifestyle modifications: This includes weight loss, dietary changes (avoiding trigger foods, smaller meals), avoiding lying down after eating, and elevating the head of the bed.
- • Medications: Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and H2 receptor antagonists are commonly prescribed to reduce stomach acid production.
- • Surgical intervention: In severe cases or when medications are ineffective, surgical procedures such as fundoplication may be considered.
-
2. Esophagitis:
- • Treatment of underlying cause: If esophagitis is caused by GERD, the management strategies mentioned above for GERD should be followed.
- • Medications: Depending on the cause, proton pump inhibitors, antifungal or antiviral drugs, or corticosteroids may be prescribed.
- • Dietary modifications: Avoiding spicy or acidic foods that can irritate the esophagus.
- • Symptomatic relief: Over-the-counter antacids or coating agents can provide temporary relief from symptoms.
-
3. Barrett's Esophagus:
- • Regular surveillance: Regular endoscopies with biopsies are performed to monitor for dysplasia or cancerous changes.
- • Medications: Proton pump inhibitors may be prescribed to reduce acid reflux and prevent further damage.
- • Surgical intervention: In cases of severe dysplasia or cancerous changes, surgical removal of the affected area may be recommended.
-
4. Esophageal Cancer:
- • Treatment depends on the stage of cancer and may involve a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy.
- • Palliative care: In advanced stages, the focus shifts to managing symptoms and improving the patient's quality of life.
-
5. Achalasia:
- • Balloon dilation: A procedure where a balloon is used to stretch and open the lower esophageal sphincter.
- • Botulinum toxin injection: Injecting botulinum toxin into the lower esophageal sphincter to relax the muscle.
- • Surgical intervention: Myotomy, a procedure that cuts the muscle of the lower esophageal sphincter, m be performed in resistant cases.
-
6. Esophageal Stricture:
- • Dilation: Stretching the narrowed area using an endoscope or bougie dilators.
- • Medications: Acid-suppressing medications may be prescribed to reduce acid reflux and inflammation.
- • Surgery: In severe cases, surgical intervention may be required to remove or bypass the narrowed segment.
It's important to note that the management of esophageal diseases should be personalized and tailored to each individual's condition. Treatment plans should be discussed with a healthcare professional who can provide a proper diagnosis and guide the management process.
Call Now
